In the world of Performance Based Navigation, RNP-1 is the new standard for terminal operations, but RNAV 1 and 2 are still in use.
— James Albright
Updated:
2020-12-14
In fact, as of late 2020, the only place you really need RNP-1 is Hong Kong. Australia requires it for their own aircraft, but not foreign aircraft. If you are going to Hong Kong, you will need an LOA or commercial specification.
1
Location
Australia
As of 26 May 2016 and where specifically promulgated, ATS Routes, Terminal Procedures and Instrument Approach Procedures should be flown to the following standard PBN Navigation Specifications:
c. Terminal Procedures (SIDs and STARs) - RNP 1.
Source: Australia AIC H13/17, ¶4.2
Exemptions are allowed for foreign registered aircraft and details are outlined in the Australia AIP. It appears they are not needed, however. Just as AIC H13/17 was being issued, the following was reported:
[AIN online, May 23, 2016]
In a last-minute about face, Australia’s Civil Aviation Safety Authority (CASA) has advised that non-commercial operators of foreign-registered aircraft that do not wish to take advantage of RNP 1 and RNP 2 traffic services that go into effect May 26 will not be required to apply for a two-year exemption to operate in Australian airspace. Only commercial operators that can comply with the requirements and want RNP 1 and RNP 2 traffic services are required to apply for an exemption.
“There is no exemption needed for foreign-registered aircraft for the foreseeable future if they are not RNP 1 and and/or or RNP 2 compliant,” according to the agency.
Starting on May 26, ATC will continue to accept aircraft that are not RNP 1 and/or RNP 2 capable as long as the operator notates on the flight plan the navigation capability of the aircraft the crew is qualified to use. Operations into Australian airspace by aircraft that are RNP 1 and RNP 2 capable and operated by qualified crew are required to flight plan in accordance with the appropriate specifications starting on May 26.
Hong Kong
3.5.3.1 Operational Approval. Any aircraft arriving or departing HKIA other than those exempted categories of flights as specified in para 3.5.3.5 shall be equipped with appropriate systems and approved by the regulatory authority of the State of Registry/State of the Operator in accordance with ICAO RNP 1 standard for the conduct of RNP 1 SID and STAR. Carriage of a certified GNSS receiver is mandatory. Aircraft or avionics manufacturers shall provide aircraft documentation that shows compliance with the applicable criteria as appropriate. RNP 1 operational approval or compliance documentation shall be readily available for Ramp or Safety Assessment of Foreign Aircraft (SAFA) inspections conducted by the Civil Aviation Department Hong Kong.
3.5.3.2 GNSS RAIM availability prediction service and the associated NOTAM information related to GNSS availability will not be provided by the Hong Kong Civil Aviation Department. In accordance with ICAO Doc 9613, PBN Manual, aircraft operators shall subscribe the necessary information provided by other service providers to verify the RAIM availability for the intended route of flight.
3.5.3.3 RNP 1 navigation specifications are listed in ICAO Doc 9613, ‘Performance-based Navigation (PBN) Manual’. The implementation procedures are given in Volume II, Part C, Chapter 3 of this document.
3.5.3.4 An operational approval issued in accordance with the ICAO Doc 9613 assumes that the operator and flight crew take into account all communication and surveillance requirements related to the relevant routes and/or airspace. Operators must therefore observe the equipment requirements when they file a flight plan. (see ENR 1.10 para. 12.3.1).
3.5.3.5 Exemption Policy. The following categories of flights are granted exemptions from the RNP 1 requirement, and approved to operate in / out of HKIA using contingency procedures stated in AD 2.22 para. 2.2.3 and para. 7.1.3:
a) Humanitarian or SAR flights;
b) State aircraft;
c) Flight Check;
d) Maintenance or delivery flights;
e) Air tests (e.g. post maintenance);
f) When specific prior approval has been given by Director-General of Civil Aviation.
3.5.3.6 Flights of categories specified in para 3.5.3.5 above shall indicate the status of flight in the flight applications to operate at HKIA, and in the FPL. Refer to ENR 1.10 para. 12.3.3 for details of flight planning requirements.
3.5.3.7 These procedures are intended exclusively for the purposes listed in para 3.5.3.5, and not as a means to circumvent the normal RNP 1 requirement.
Source: Hong Kong AIP, GEN 1.5-2, ¶3.5.3 RNP 1 SID / STAR
2
Accuracy / performance standards
The following examples are provided for the RNP 1 specification:
Accuracy: During operations in airspace or on routes designated as RNP 1, the lateral TSE must be within ±1 NM for at least 95 per cent of the total flight time. The along-track error must also be within ±1 NM for at least 95 per cent of the total flight time.
Integrity: Malfunction of the aircraft navigation equipment is classified as a major failure condition under airworthiness regulations (i.e. 10–5 per hour).
Continuity: Loss of function is classified as a minor failure condition if the operator can revert to a different navigation system and proceed to a suitable airport.
On-board performance monitoring and alerting: The RNP system, or the RNP system and pilot in combination, shall provide an alert if the accuracy requirement is not met, or if the probability that the lateral TSE exceeds 2 NM is greater than 10–5.
SIS: If using GNSS, the aircraft navigation equipment shall provide an alert if the probability of SIS errors causing a lateral position error greater than 2 NM exceeds 10–7 per hour.
Source: ICAO Doc 9613, Volume II, Part A, ¶2.3.13
3
Operational approval
This used to be a mess for Part 91 operators wanting to fly to Hong Kong because the U.S. FAA said no LOA needed, Hong Kong said it was. At first the FAA refused to issue the LOA, and then they would if you could prove you are flying to Hong Kong. I think that is resolved as we've seen operators get the LOA without too much trouble.
Part 91 Operators
A letter of authorization (LOA) is not required for Title 14 of the Code of Federal Regulations (14 CFR) part 91 operators (other than part 91 subpart K (part 91K)) except for oceanic operations (see Appendices E, F, and G) or if required in foreign airspace. Part 91 operators (other than 91K) should comply with the aircraft eligibility and operational guidance in this advisory circular (AC).
Source: AC 90-105A, ¶7.1
Parts 91K, 121, 125, 129, and 135 Operators
Title 14 CFR parts 91K, 121, 125, 129, and 135 operators receive approval to fly RNP operations as described in this AC via operations specifications (OpSpecs), management specifications (MSpecs), or LOAs as follows:
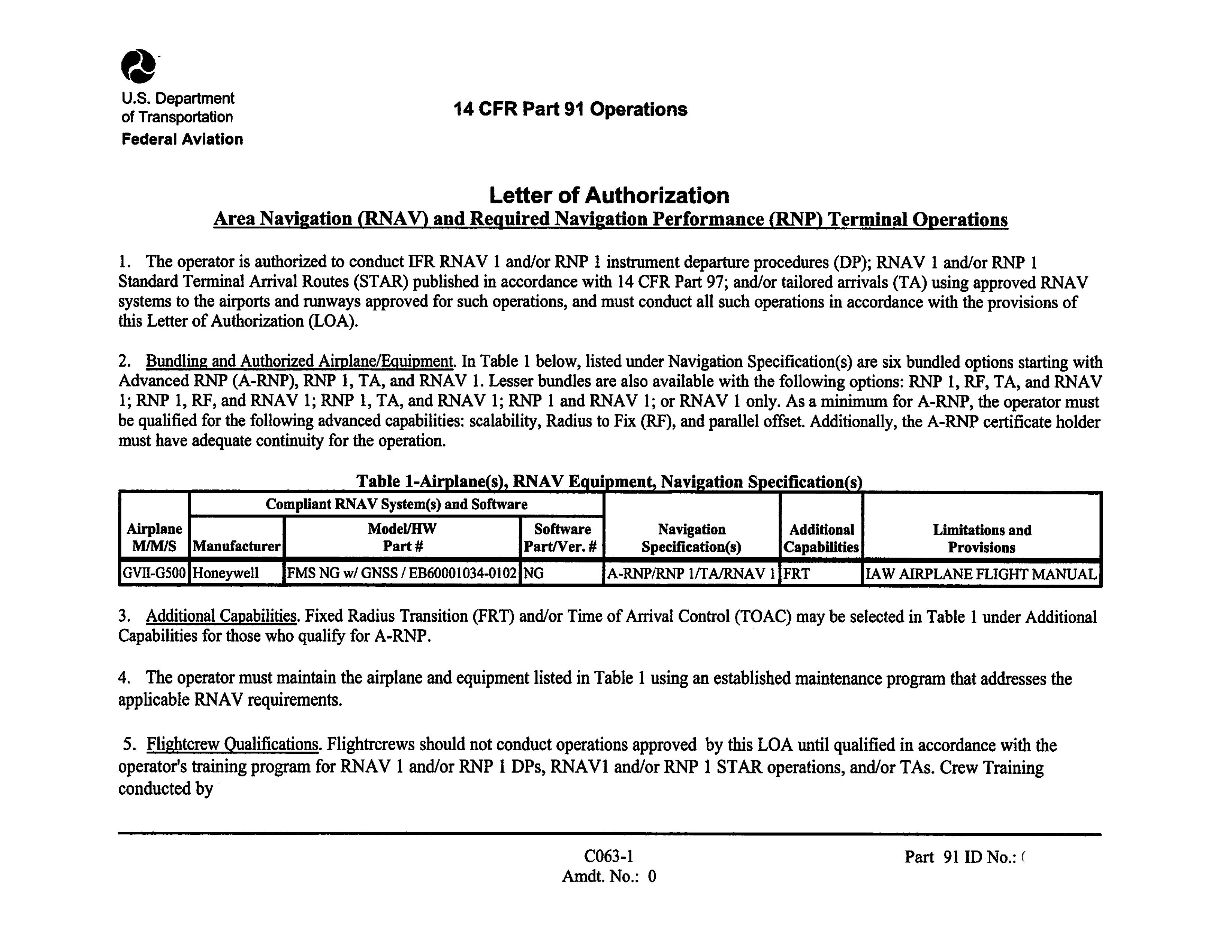
- OpSpec/MSpec/optional LOA, paragraph C063, Area Navigation (RNAV) and Required Navigation Performance (RNP) Terminal Operations;
- OpSpec/MSpec, paragraph B035, Class 1 Navigation in U.S. Class A Airspace Using Area or Long-Range Navigation Systems;
- OpSpec/MSpec/LOA (to include Part 91 operators), paragraph B036, Oceanic and Remote Continental Navigation Using Multiple Long-Range Navigation Systems(M-LRNS); or
- Helicopter Specification (HSpec)/LOA, paragraph H123, Class I Navigation Using Area or Long-Range Navigation Systems with Wide Area Augmentation System(WAAS) for Rotorcraft Required Navigation Performance (RNP) 0.3 En Route and Terminal Operations.
Source: AC 90-105A, ¶7.3
References
(Source material)
Australia Aeronautical Information Circular H13/17, Effective 201705241600 UTC
Australia Aeronautical Information Publication, 5 Nov 2020
Hong Kong Aeronautical Information Publication, 30 Jan 2020
Advisory Circular 90-105A, Approval Guidance for RNP Operations and Barometric Vertical Navigation in the U.S. National Airspace System and in Oceanic and Remote Continental Airspace, 3/7/2016, U.S. Department of Transportation
FAA Orders 8400 and 8900
ICAO Doc 9613 - Performance Based Navigation (PBN) Manual, International Civil Aviation Organization, Fourth Edition, 2013